So I’ve heard a lot of people say they are so fascinated by what I do in the process improvement world, and how great they think it is , but how “it’s not for them”. Using my coaching skills, I usually say something like, “Oh yeah? Tell me about why it isn’t for you”.
Here are some of the responses I get:
“Snore. Processes are super boring. My company is really intuitive, and we just know exactly what to do and we fix it.” – my super annoying friend
“Processes, who needs it? I already know my team is garbage and as soon as I can replace them, things will turn around”. – a client who later realized her team was great because process mapping revealed a culture issue
“Ugh. Sounds bureaucratic. I’m an entrepreneur. There is nothing corporate about he way I run my business, and to be honest we don’t need it.” – my sister-in-law
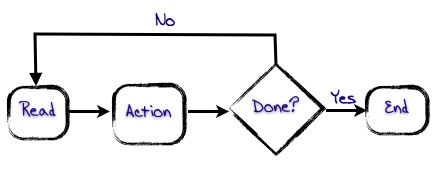
 3 Signs You Need Process Mapping STAT!
3 Signs You Need Process Mapping STAT!
- Something is wrong and you “think” know exactly how to fix it. How do you know what’s wrong? What leads you to believe that? What is the expected outcome if you make the change? You might be right. Intuition is super important. Why not validate those gut feelings with some evidence in a process map? It’s a great way to get buy in from your stakeholders and employees!
- You “think” your employees are the problem. They suck. While this is the first place many people look for solutions, it’s usually something else. Why do you think they suck? What tells you that? What could be inhibiting them? Have you asked them? Research shows that if you take great people and put them in a bad process, the process will win every time. Process mapping sometimes uncovers secrets that are hiding within a bad process.
- You “think” process is too rigorous. Well, it can be, but it doesn’t have to be. The right people, the right style, and the right moment can take you from being a fly-by-the-seat-of-your-pants entrepreneur to a being a strategic one. Why not set the stage so you can pass the tasks that aren’t worth your time (or you aren’t great at) to someone who can actually add value (so you can go and be amazing). Process mapping identifies those tasks and lets you properly divide them up.
If you’re not a “process person,” or even if you are but don’t have a lot of time, we can help you. We are expert at coming in, talking with you and your team, and uncovering the hidden opportunities to improve your business.
Even better – why not build process improvement and process mapping capacity on your team? We offer public workshops that are fun, interactive, and relevant. Check them out by clicking here, and contact us if you want to know more.
#whiteboardworskhops #theyredifferent
Until Next Time,
Nicole




 Process Mapping is awesome and fun and helpful and easy and so amazing, right?
Process Mapping is awesome and fun and helpful and easy and so amazing, right? Whiteboard Workshop: Introduction to Process Mapping
Whiteboard Workshop: Introduction to Process Mapping